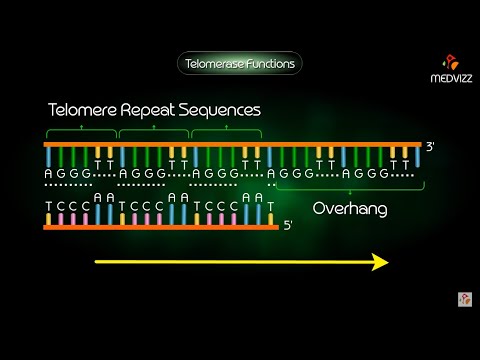
Subtitles & vocabulary
Telomerase Function - Animation
00
吳佳盈 posted on 2024/07/07Save
Video vocabulary
process
US /ˈprɑsˌɛs, ˈproˌsɛs/
・
UK /prə'ses/
- Transitive Verb
- To organize and use data in a computer
- To deal with official forms in the way required
- Noun (Countable/Uncountable)
- Dealing with official forms in the way required
- Set of changes that occur slowly and naturally
A2TOEIC
More exact
US /ɪɡˈzækt/
・
UK /ɪɡ'zækt/
- Adjective
- Completely correct; accurate; specific
- Transitive Verb
- To get something, sometimes using force
A2TOEIC
More complex
US /kəmˈplɛks, ˈkɑmˌplɛks/
・
UK /'kɒmpleks/
- Countable Noun
- Group of buildings all used for the same purpose
- Adjective
- Not being simple; having many parts or aspects
A2
More unique
US /juˈnik/
・
UK /jʊ'ni:k/
- Adjective
- Unlike other things; being the only one like it
- Remarkably special or unusual.
A2TOEIC
More Use Energy
Unlock Vocabulary
Unlock pronunciation, explanations, and filters
