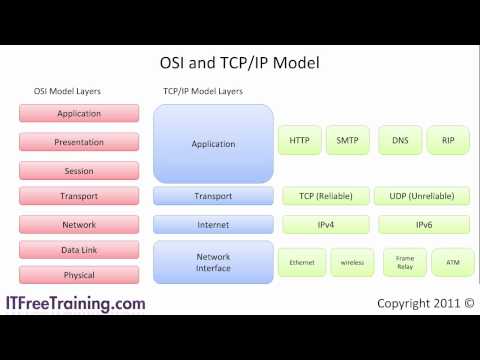
Subtitles & vocabulary
Video vocabulary
physical
US /ˈfɪzɪkəl/
・
UK /ˈfɪzɪkl/
- Countable Noun
- Health check at the doctors' or hospital
- Adjective
- Concerning the body of a person
- Concerning things that can be seen or touched
A2
More layer
US /ˈleɚ/
・
UK /ˈleiə/
- Noun (Countable/Uncountable)
- One of several sheets of a material or object
- A covering of something spread over a surface.
- Transitive Verb
- To put things one on top of another
B1TOEIC
More presentation
US /ˌprɛzənˈteʃən, ˌprizən-/
・
UK /ˌpreznˈteɪʃn/
- Noun (Countable/Uncountable)
- Act of giving a formal talk about something
- Way in which something is displayed or shown
A2
More understand
US /ˌʌndɚˈstænd/
・
UK /ˌʌndə'stænd/
- Verb (Transitive/Intransitive)
- To know the meaning of language, what someone says
- To be aware of something
A1
More Use Energy
Unlock Vocabulary
Unlock pronunciation, explanations, and filters
