Subtitles & vocabulary
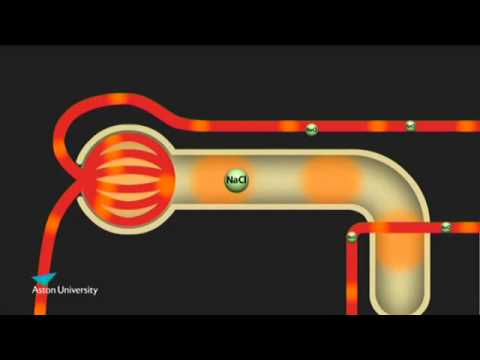
The Kidney & the Counter Current Multiplier: Pharmacology teaching at Aston University
00
柳夙芯 posted on 2017/01/12Save
Video vocabulary
potential
US /pəˈtɛnʃəl/
・
UK /pəˈtenʃl/
- Adjective
- Capable of happening or becoming reality
- Having or showing the capacity to develop into something in the future.
- Uncountable Noun
- someone's or something's ability to develop, achieve, or succeed
A2TOEIC
More entire
US /ɛnˈtaɪr/
・
UK /ɪn'taɪə(r)/
- Adjective
- Complete or full; with no part left out; whole
- Undivided; not shared or distributed.
A2TOEIC
More essentially
US /ɪˈsenʃəli/
・
UK /ɪˈsenʃəli/
- Adverb
- Basically; (said when stating the basic facts)
- Used to emphasize the basic truth or fact of a situation.
A2
More eventually
US /ɪˈvɛntʃuəli/
・
UK /ɪˈventʃuəli/
- Adverb
- After a long time; after many attempts; in the end
- At some later time; in the future
A2
More Use Energy
Unlock Vocabulary
Unlock pronunciation, explanations, and filters
